Internal Carotid Artery Calcified Plaque With Acoustic Shadow: What to Do?
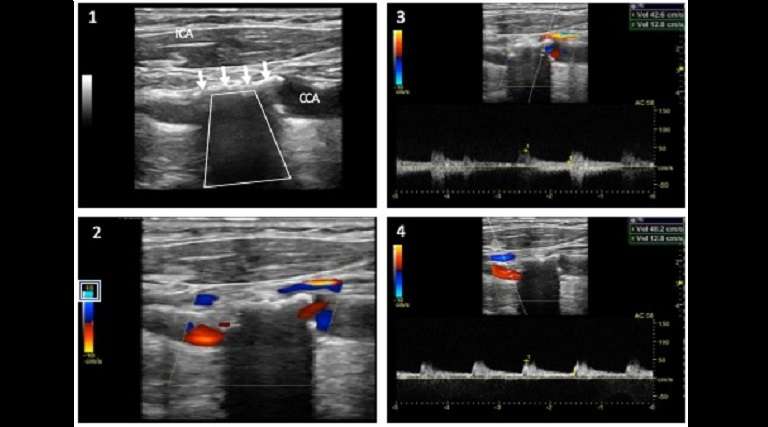
Case study description: Image case study — ICA and acoustic shadow
Image case study: No video or audio
The main objective of the supra aortic arteries ultrasound examination is to rule out the presence of stenoses at the level of the carotid and vertebral arteries.
However, the presence of calcified atherosclerotic plaques can reduce the ultrasound sensitivity and specificity in detecting and grading stenoses of these vessels.
Calcified plaques often reflect ultrasound, thus, causing an acoustic shadowing which may limit the assessment of the intraluminal extension of the plaque and the reliability in grading the eventual presence of a stenosis.
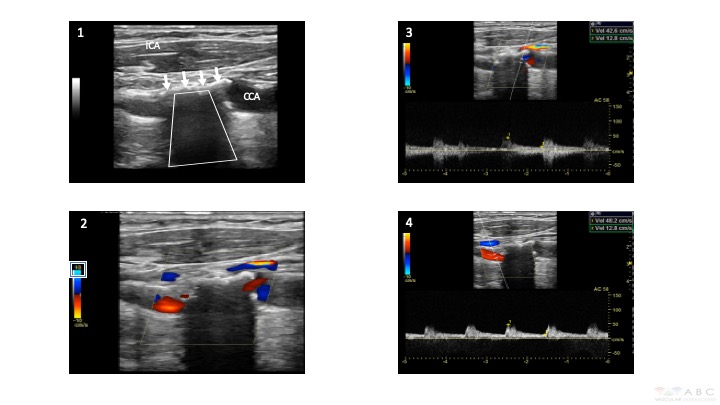
Figure 1 shows a typical calcified plaque, appearing hyperechoic (white) in B-mode (white arrows) and causing an acoustic shadowing (trapezoid shape) at the level of the origin and proximal region of the internal carotid artery (ICA).
Figure 2 shows the colour Doppler flow appearance of the ICA calcified plaque. Colour flow is seen before and after the acoustic shadowing, however no colour flow is observed below the acoustic shadow. In this case lowering the colour scale may reveal to be useful in order to visualise flow through this region (see colour scale value). Sometimes the use of a curvilinear array may help in visualising flow through this region.
Figure 3 shows the peak systolic (PSV) and end diastolic (EDV) velocities measured before the acoustic shadow. Figure 4 shows the PSV and EDV velocities measured after the acoustic shadow. These velocities are normal (PSV < 125 cm/sec, EDV < 40 cm/sec) and the lack of velocities changes before and after the acoustic shadow, suggest, but cannot rule out, the absence of significant stenoses at these levels. However, as the presence of a significant stenosis of the actual shadowed segment cannot be ruled out, the examiner should suggest the use of alternative imaging, in particular in those cases in which the extension of the acoustic shadow is longer than 1 cm.